-
Original Article
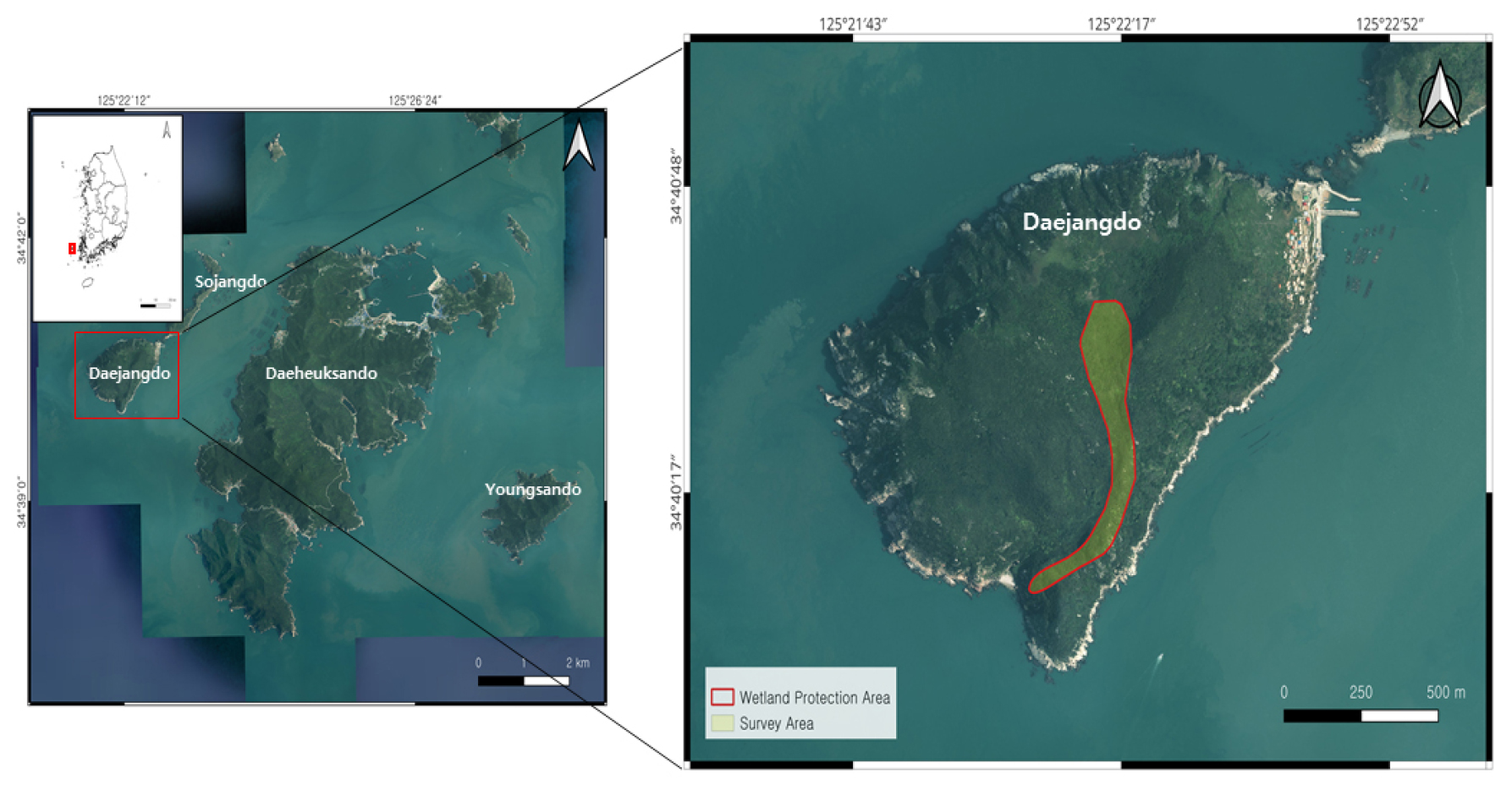
-
Analysis of Flora Changes and Management Plan for the Shinan Jangdo Mountain Wetland Protected Areas, Daejangdo Island, South Korea
신안 장도 산지습지 습지보호지역의 식물상 변화 및 관리방안 연구
-
Sangwook Han, Inchun Hwang, Myeongho Shim, Minhyeok Won, Sanghoon Lee, Suhwan Kim
한상욱, 황인천, 심명호, 원민혁, 이상훈, 김수환
- This study analyzed survey data from 2018 and 2024 to identify plant diversity and changes in flora in the Shinan Jangdo Mountain …
본 연구는 신안 장도 산지습지 습지보호지역의 식물다양성과 식물상 변화를 파악하고 관리방안을 제시하고자 2018년과 2024년의 조사자료를 분석하였다. 총 328분류군이 확인되었으며, 습지식물은 네모골 등 …
- This study analyzed survey data from 2018 and 2024 to identify plant diversity and changes in flora in the Shinan Jangdo Mountain Wetland Protected Area and to suggest management measures. A total of 328 taxa were identified, and 35 wetland plant taxa, including Eleocharis tetraquetra, showed that the hydrological and soil environments of mountain wetlands were stably maintained. Four taxa of endemic plants, including the Indigofera koreana, were identified, and eight taxa of rare plants, including the Athyrium sheareri, were identified. In particular, the Class II Endangered Wild Species, the Dendrobium moniliforme, was newly discovered in 2024, demonstrating its high conservation value. Climate change plants include a total of 43 taxa, including Machilus thunbergii, and among them, the proportion of complex sensitive species is high, so it is judged that there is a high possibility of habitat changes due to future climate change. Analysis of flora similarity with surrounding islands revealed the highest similarity with Yeongsan Island, confirming regional ecological connectivity. The influx of some alien and invasive plants has been observed, necessitating ongoing management. Systematic management strategies, including the establishment of key conservation areas and the removal of invasive plants, are necessary. This study quantitatively presents the characteristics of changes in the flora of the Shinan Jangdo Mountain Wetland, which can be used as basic data for future wetland conservation policies.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 신안 장도 산지습지 습지보호지역의 식물다양성과 식물상 변화를 파악하고 관리방안을 제시하고자 2018년과 2024년의 조사자료를 분석하였다. 총 328분류군이 확인되었으며, 습지식물은 네모골 등 35분류군으로 산지습지의 수문 및 토양환경이 안정적으로 유지되고 있음을 보여주었다. 특산식물은 좀땅비싸리 등 4분류군, 희귀식물은 개톱날고사리 등 8분류군이 확인되었다. 특히, 멸종위기 야생생물 Ⅱ급 석곡은 2024년에 서식이 새롭게 확인되어 보전 가치가 높은 것으로 확인되었다. 기후변화식물은 후박나무 등 총 43분류군으로 이 중 복합 민감형 종의 비율이 높아 향후 기후변화에 따른 서식지 변동 가능성이 클 것으로 판단된다. 주변 도서지역과의 식물상유사도 분석 결과 영산도와의 유사도가 가장 높아 지역 생태적 연계성이 확인되었다. 일부 외래식물 및 생태계교란 식물의 유입이 관찰되어 지속적 관리가 요구되며, 핵심보전구역 설정과 교란식물 제거 등 체계적 관리전략 마련이 필요하다. 본 연구를 통하여 신안 장도 산지습지 식물상 변화 특성을 정량적으로 제시해 향후 습지보전 정책의 기초자료로 활용될 수 있다.
-
Analysis of Flora Changes and Management Plan for the Shinan Jangdo Mountain Wetland Protected Areas, Daejangdo Island, South Korea
-
Original Article
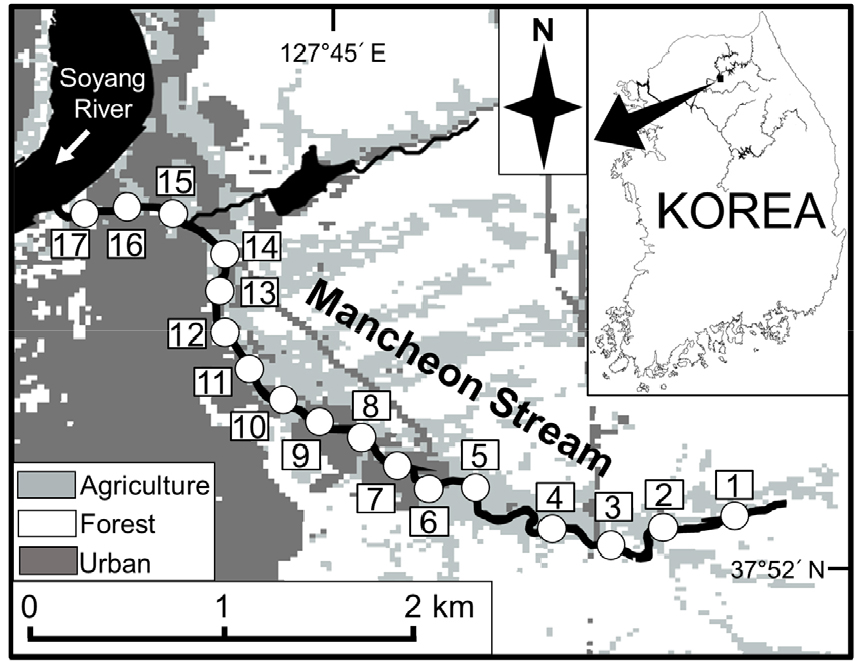
-
Effects of Environmental Factors on Fish Biodiversity in a Small-Sized Urban Stream
소형 도시하천에서 환경 요인이 어류 종 다양성에 미치는 영향
-
Gyurin Lee, Seunghwan Park, Sunam Kim, Jeongwon Lee, Min Heo, Seoghyun Kim
이규린, 박승환, 김수남, 이정원, 허민, 김석현
- Small-sized urban streams often exhibit reduced biodiversity patterns due to multiple disturbances and habitat degradation. To identify key environmental factors affecting fish …
도시지역을 관류하는 소형 하천은 다양한 교란 및 훼손에 의해 낮은 생물 다양성을 가진다. 따라서 소형 도시하천에서 종 다양성에 영향을 주는 핵심적인 환경 …
- Small-sized urban streams often exhibit reduced biodiversity patterns due to multiple disturbances and habitat degradation. To identify key environmental factors affecting fish diversity, which can provide insight into ecosystem management and restoration actions in urban streams, we investigated Mancheon Stream, a small-sized urban stream located at Chuncheon, Gangwon State, Korea. Fish sampling and environmental measurement were conducted at 17 sites from headwater to confluence with Soyang River between November 2023 and August 2024. A total of 23 species belonging to 7 families were collected during the study period. Results of a hierarchical cluster analysis and a non-metric multidimensional scaling showed that 17 study sites were categorized by three groups, while both species richness and diversity indexes increased gradually in the downstream direction. The result of a linear mixed-effects model revealed that fish diversity increased with the size of the stream and was associated positively with in-channel vegetation. In addition, lotic habitats, such as runs and riffles, were also an important component for increasing fish diversity. Our results highlight that establishing natural physical habitats would be a key step for successful management and restoration of aquatic biodiversity in small-sized urban streams.
- COLLAPSE
도시지역을 관류하는 소형 하천은 다양한 교란 및 훼손에 의해 낮은 생물 다양성을 가진다. 따라서 소형 도시하천에서 종 다양성에 영향을 주는 핵심적인 환경 요인을 분석함으로써 도시 생태계 건강성 회복 및 복원을 위한 연구가 시급한 실정이다. 본 연구는 강원특별차지도 춘천시에 위치한 소형 도시하천인 만천천에서 환경이 어류의 종 다양성에 미치는 영향을 연구하였다. 만천천 상류부터 소양강 합류지점까지 17개 조사지점에서 2023년 11월부터 2024년 8월까지 어류 조사 및 환경 측정을 수행하였다. 조사기간 동안 출현한 어류는 7과 23종이었다. 계층적 군집분석(hierarchical cluster analysis)과 비모수다차원척도법(non-metric multidimensional scaling)을 사용하여 어류군집 구조를 분석한 결과, 조사지점은 3개의 집단으로 구분되었으며 종 풍부도와 종 다양도는 하류로 갈수록 높아짐을 확인하였다. 선형 혼합 모형(linear mixed-effect model)을 사용하여 환경 요인이 어류 종 다양성에 미치는 영향을 분석한 결과, 하천의 규모가 커질수록 종 다양성이 높아지는 동시에 하도 내 식생이 발달할수록 종 풍부도와 종 다양도가 증가하는 경향을 확인하였다. 또한 물 흐름이 있는 유수환경 조성이 종 다양성 증가에 중요한 역할을 했다. 본 결과는 자연적인 환경 조성을 통해 어류 서식처를 제공하는 것이 도시하천 생태계 복원 및 생물 다양성을 보전하는 데에 있어 중요하다는 것을 보여주고 있다.
-
Effects of Environmental Factors on Fish Biodiversity in a Small-Sized Urban Stream
-
Original Article
-
National-Scale Estimation and Feasibility Assessment of Environmental Flows Using Maximum Weighted Usable Area
최대 가중가용면적을 이용한 전국 단위 환경생태유량 산정과 확보 가능성 평가
-
Soohong Kim, Hyeongsik Kang, Inhong Song, Eunmi Hong
김수홍, 강형식, 송인홍, 홍은미
- This study estimated ecological flows (EF) at vulnerable sites across the nation and evaluated their attainability. The PHABSIM model was applied to …
본 연구는 전국의 취약지점을 대상으로 환경생태유량을 산정하고 그 확보 가능성을 평가하였다. PHABSIM 모형을 적용하여 지점별 대표 어종에 따른 최적 환경생태유량을 도출하였으며, 이를 …
- This study estimated ecological flows (EF) at vulnerable sites across the nation and evaluated their attainability. The PHABSIM model was applied to derive the optimal EF for representative fish species at each site, and the results were compared with flow regime indicators–low flow (Q355), subnormal flow (Q275), and normal flow (Q185). In addition, deficiency days (periods when EF was not met) were calculated for each site and river basin using hydrological data from 2015–2024. The analysis revealed that EF values at most sites were estimated above the normal flow, indicating that higher discharges than those suggested by conventional flow regimes are required to sustain riverine ecosystems. In contrast, several upstream sites exhibited almost no deficiency days, suggesting that ecological flows can remain relatively stable even during low-flow periods. These basin- and site-specific differences appear to reflect a combination of factors, including longitudinal position (upstream–downstream), the presence of artificial structures, and hydrological characteristics of the basins. This study is among the first nationwide efforts to quantify EF and incorporate deficiency-day analysis to evaluate the practical attainability of ecological flows. The findings provide fundamental insights for river management and ecological flow policies.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 전국의 취약지점을 대상으로 환경생태유량을 산정하고 그 확보 가능성을 평가하였다. PHABSIM 모형을 적용하여 지점별 대표 어종에 따른 최적 환경생태유량을 도출하였으며, 이를 갈수량(Q355), 저수량(Q275), 평수량(Q185)과 비교하였다. 또한 2015–2024년 유량 자료를 활용하여 지점별·권역별 부족일수(최적 환경생태유량에 도달하지 못한 기간)를 산정하였다. 분석 결과, 대다수의 지점에서 환경생태유량이 평수량 이상의 범위로 산정되어 하천 생태계 보전을 위해 기존 평수량보다 높은 유량이 필요함을 알 수 있었다. 일부 상류 지점에서는 부족일수가 거의 발생하지 않아 갈수기에도 비교적 안정적으로 생태유량이 확보되는 것으로 확인되었다. 이러한 권역별·지점별 편차는 상·중·하류 위치, 인공 구조물의 영향, 수문 체계 특성 등 복합적인 요인에서 기인한 것으로 해석된다. 본 연구는 전국 단위에서 환경생태유량을(Ecological Flow, EF) 정량적으로 산정하고 부족일수 분석을 도입하여 실제 유량 확보 가능성을 평가한 최초의 사례 중 하나로서, 하천 생태유량 관리의 기초 자료를 제공한다는 점에서 의의가 있다.
-
National-Scale Estimation and Feasibility Assessment of Environmental Flows Using Maximum Weighted Usable Area
-
Original Article
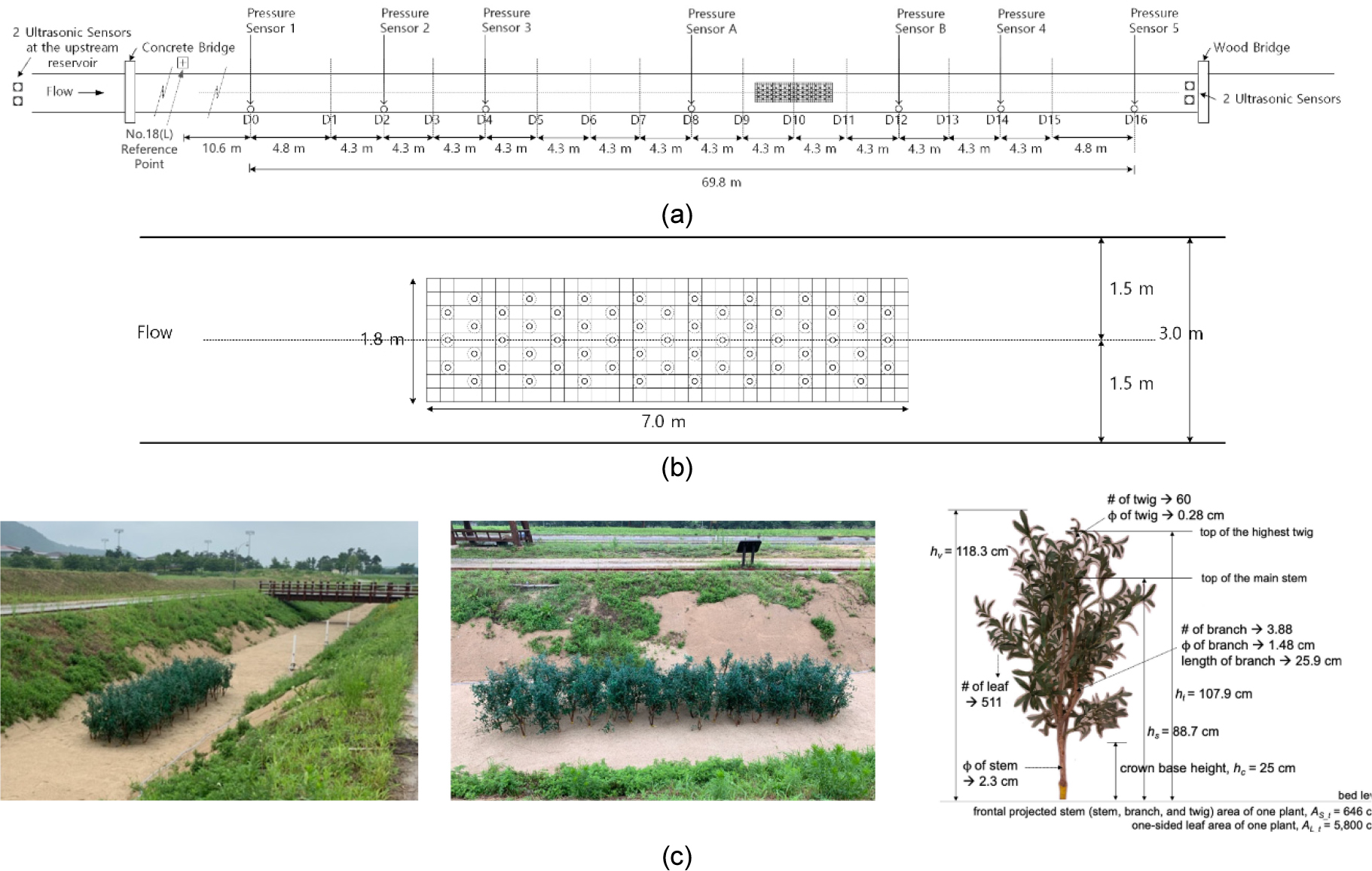
-
Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Bed Morphology and Grain-size Distribution Changes around a Woody Vegetation Patch in a Large-scale River Experiment
실규모 하천 실험을 통한 목본성 식생패치 주변의 시공간적 하상변동 및 하상토 입도 분포 변화 분석
-
Eunkyung Jang, Un Ji
장은경, 지운
- This study quantitatively analyzed bed morphological changes around an artificial vegetation patch in a large-scale outdoor flume from spatial, temporal, and material …
본 연구에서는 대규모 야외 수로에서 인공 식생패치를 설치하고, 실험 전후 하상변동을 공간·시간·재료적 관점에서 정량적으로 분석하였다. 드론 영상과 3차원 레이저 스캐너 자료의 비교 …
- This study quantitatively analyzed bed morphological changes around an artificial vegetation patch in a large-scale outdoor flume from spatial, temporal, and material perspectives. Comparison of drone imagery and 3D laser scanning data revealed contrasting spatial patterns: pronounced scour at the patch front (near the upstream boundary) and concentrated deposition in the wake region (approximately 3-5 times the patch length downstream). Time-series observations using acoustic-based monitoring showed rapid initial scour followed by progressive stabilization, with sediment accumulation in the wake zone over time. Grain-size analysis further indicated heterogeneous material responses. At lateral locations of the vegetation patch, fines were reduced and coarsening was observed, whereas the patch interior and wake region showed increased fines and fining. Both the uniformity coefficient and curvature coefficient decreased overall, suggesting a general tendency toward homogenization of sediment distribution. These findings demonstrate that vegetation patches act not merely as flow-disturbing obstacles but as key drivers that structurally reorganize bed morphology and sediment sorting characteristics. The study provides experimental evidence of vegetation-bed interactions under full-scale conditions and offers baseline data for vegetated channel management and river restoration strategies.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 대규모 야외 수로에서 인공 식생패치를 설치하고, 실험 전후 하상변동을 공간·시간·재료적 관점에서 정량적으로 분석하였다. 드론 영상과 3차원 레이저 스캐너 자료의 비교 분석 결과, 식생패치 전면부(상류 측 경계부근)에서는 뚜렷한 세굴이, 식생패치 후류영역(하류 측 약 식생패치 길이의 3~5배 범위)에서는 퇴적이 집중적으로 발생하는 상반된 공간적 하상형태가 확인되었다. 음향 기반 모니터링을 통한 시계열 관측에서는 실험 초기의 급격한 세굴과 시간이 지남에 따라 후류영역에서 퇴적이 누적되며 변화 양상이 점차 안정화되는 과정이 관찰되었다. 또한 지점별 입도 분석 결과, 식생패치 측면 지점에서는 세립분이 감소하여 조립화가 진행된 반면, 내부와 후류영역에서는 세립분이 증가하는 세립화가 나타났다. 균등계수와 곡률계수는 전반적으로 감소하여 입도 분포가 균질화 되는 경향이 확인되었다. 이러한 결과는 식생패치가 단순한 흐름 교란 요소를 넘어, 국지적인 하상 형성과 재료 분급 특성을 구조적으로 재편성하는 핵심 인자임을 보여준다. 본 연구는 실규모 조건에서 식생–하상 상호작용을 정량적으로 규명하였다는 점에서 학술적 의의가 있으며, 식생하천 관리 및 하천복원 전략 수립에 필요한 기초 자료를 제공한다.
-
Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Bed Morphology and Grain-size Distribution Changes around a Woody Vegetation Patch in a Large-scale River Experiment
-
Original Article
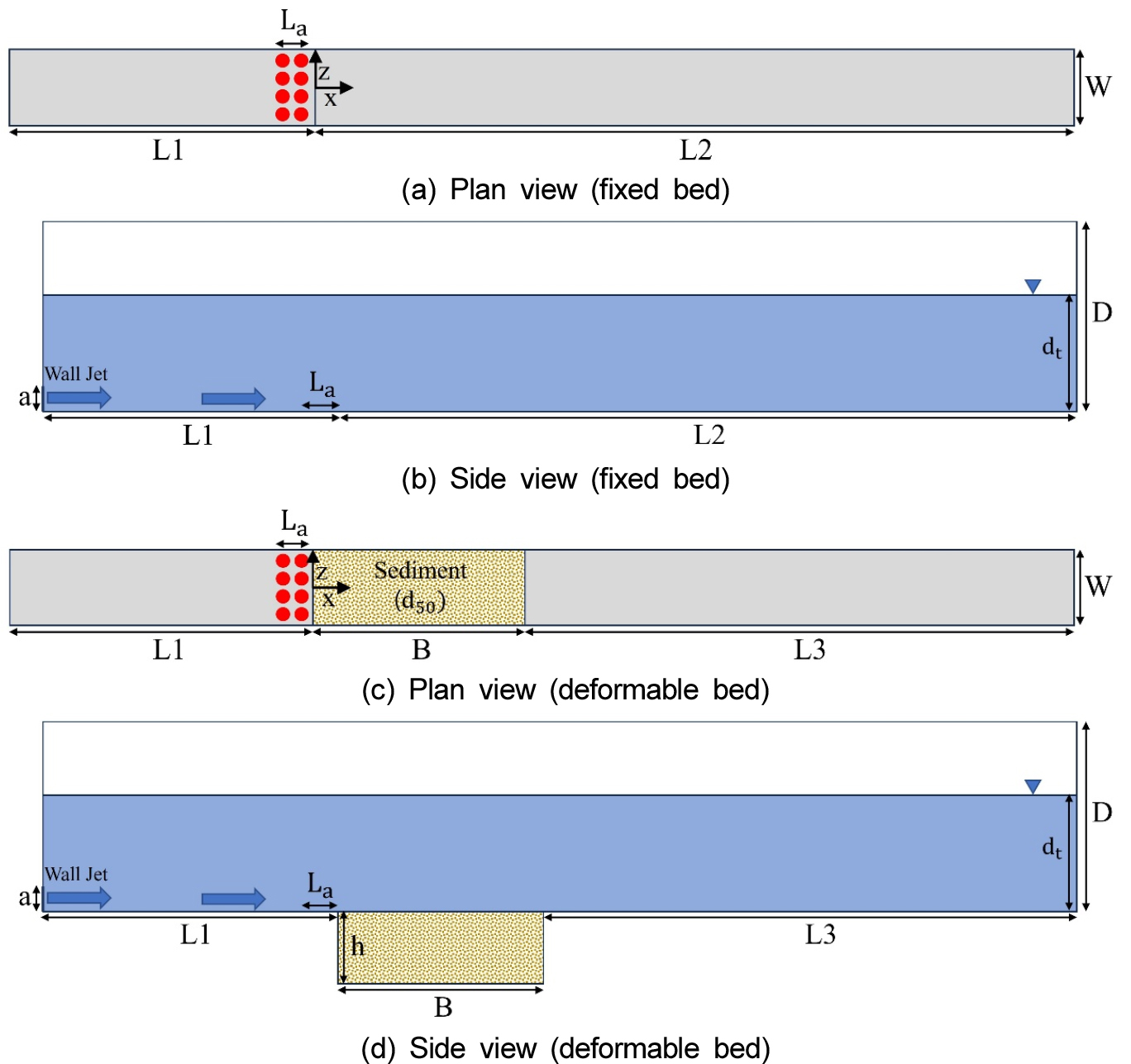
-
Effectiveness Analysis of a Vertical Water-Injection Technique for Scour Mitigation Immediately Downstream of the Apron
물받이공 직하류 세굴 저감을 위한 연직 물 주입 기법의 효과 분석
-
Jeong Hu Lee, Chang Geun Song
이정후, 송창근
- The local scour downstream of a rigid apron, caused by submerged wall jets from sluice gate openings, is critically important as it …
수문 개구부를 통해 방류되는 수중 벽제트는 보 하도 하류에서 국부 세굴을 유발하며, 이는 수공 구조물의 안정성을 위협하는 주요 요인 중 하나이다. 본 …
- The local scour downstream of a rigid apron, caused by submerged wall jets from sluice gate openings, is critically important as it poses a significant threat to structural stability. This study examines the impact of water injection at the apron’s end on flow structures and scour mitigation under a wall jet flow. A coupled numerical model for scour simulation was developed by integrating the Large Eddy Simulation (LES) model, the Discrete Element Method (DEM), and the Volume of Fluid (VOF) method within the open-source CFD software OpenFOAM. Validation of the numerical model shows a good agreement between the simulation results and observed data, confirming the model’s reliability. The numerical model was used to analyze the quantitative changes in flow structures and scour morphology by increasing the vertical water injection flow rate ratio (defined as the ratio of injection flow rate to the wall jet flow rate) from 0 to 0.25. The results indicated that as the injection flow rate ratio increased, the streamwise mean velocity and bed shear stress near the apron decreased, leading to significant reductions in both bedload transport rate and maximum scour depth. Specifically, when the injection flow rate ratio was 0.1, 0.2, and 0.25, the maximum scour depth was reduced by 40.82%, 63.27%, and 95.92%, respectively. These findings demonstrate that vertical water injection at the downstream end of the apron can serve as an effective countermeasure for local scour mitigation. Compared to conventional scour protection techniques, this method offers greater flexibility and adaptability in hydraulic structure design. Future research will investigate the scour reduction effects under various flow conditions and configurations of injection slot geometry.
- COLLAPSE
수문 개구부를 통해 방류되는 수중 벽제트는 보 하도 하류에서 국부 세굴을 유발하며, 이는 수공 구조물의 안정성을 위협하는 주요 요인 중 하나이다. 본 연구에서는 벽제트 흐름 하에서 하도 종단에서의 연직 물 주입이 유동 구조 및 세굴 저감에 미치는 영향을 수치적으로 분석하였다. 이를 위해, 3차원 계산유체역학 소프트웨어인 OpenFOAM을 기반으로, LES (Large Eddy Simulation) 난류 모형, DEM (Discrete Element Method) 기법, VOF (Volume of Fluid) 기법을 통합한 결합 세굴 수치모형을 구축하였다. 구축된 수치모형을 통해 얻은 유동 구조 및 세굴 형상 결과를 실험 자료와 비교한 결과, 양호한 일치도를 보여 모형의 신뢰성을 확보하였다. 수치모형을 이용하여 개구부 방류 체적 유량에 대한 물 주입 유량비를 0에서 0.25까지 단계적으로 증가시키며 유동 구조 및 세굴 형상의 정량적 변화를 분석하였다. 그 결과, 물 주입 유량비가 증가할수록 하도 인근 흐름 방향 평균 유속과 바닥 전단응력이 감소하였으며, 이에 따라 소류사 이송률과 세굴심 모두 유의미하게 저감되는 경향을 보였다. 결과적으로, 개구부 방류 체적 유량에 대한 물 주입 유량비가 0.1, 0.2, 0.25일 때, 최대 세굴심은 각각 40.82%, 63.27%, 95.92% 감소하는 것으로 나타났다. 본 연구의 주요 결론은 하도 종단에서의 물 주입이 하류 세굴 저감에 효과적인 수단이 될 수 있으며, 기존의 세굴 저감 대책들에 비해 수공 구조물 설계에 있어 보다 높은 유연성과 대응력을 제공할 수 있음을 보여준다는 점이다. 향후 연구에서는 다양한 유동 조건 및 주입 슬롯 구성 변화에 따른 세굴 저감 효과를 추가적으로 분석할 계획이다.
-
Effectiveness Analysis of a Vertical Water-Injection Technique for Scour Mitigation Immediately Downstream of the Apron
-
Original Article
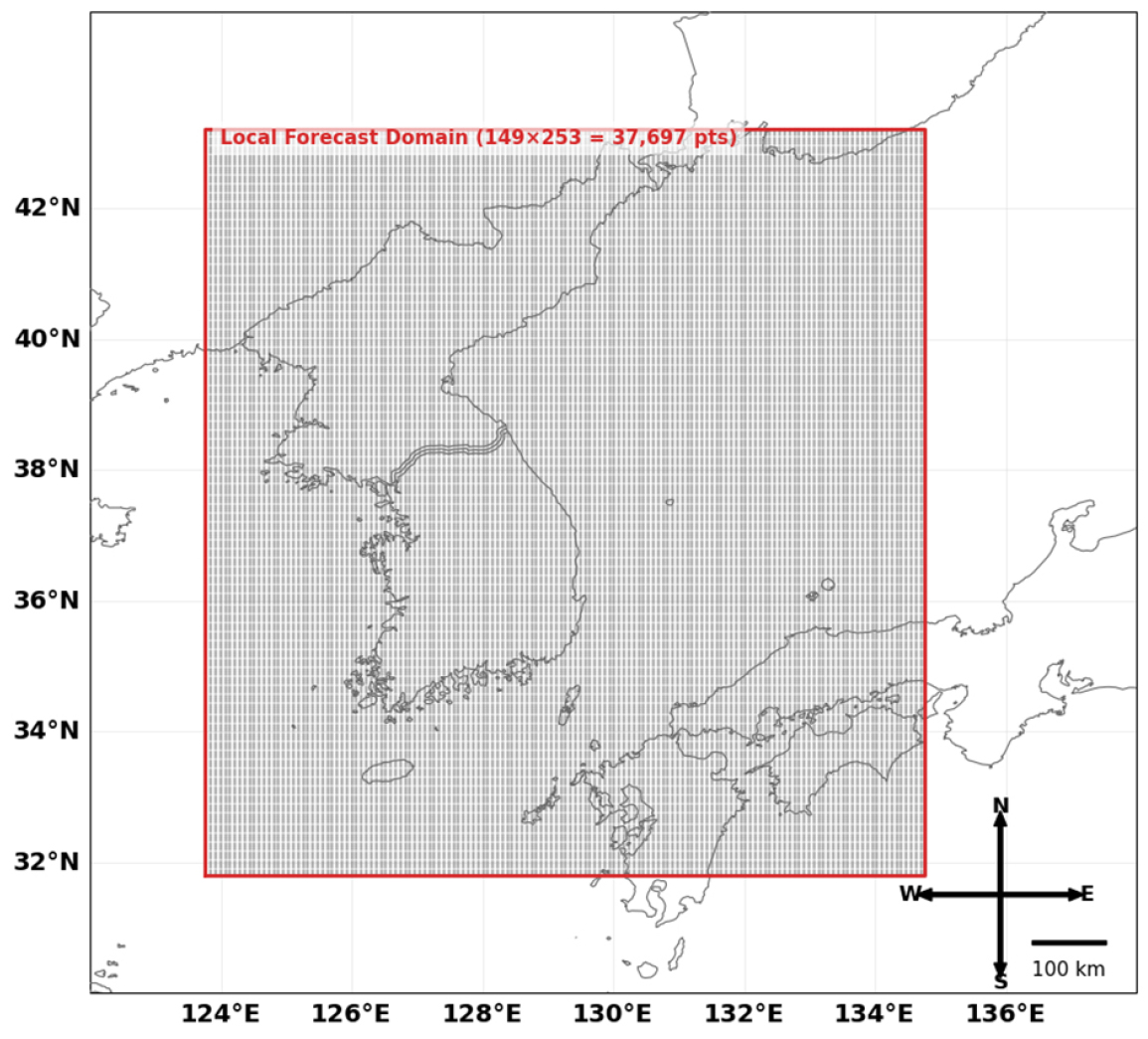
-
Convolutional Neural Network-Based Weather Forecasting Post-Processing Method Using Short-Term Neighborhood Forecast Data
단기예보 데이터를 활용한 Convolutional Neural Network 기반 다지점 단기강수예측 정보 보정 기법 개발
-
Sangbeom Jang, Ju-Young Shin, Sunghun Kim, Yongseok Kim
장상범, 신주영, 김성훈, 김용석
- This study developed a short-term precipitation forecasting correction technique using a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) based on the Korea Meteorological Administration’s Local …
본 연구는 기상청의 동네예보 자료를 대상으로 합성곱 신경망(Convolutional Neural Network, CNN)을 활용하여 단기 강수 예측 정보 보정 기법을 개발하였다. 동네예보는 복잡한 지형과 …
- This study developed a short-term precipitation forecasting correction technique using a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) based on the Korea Meteorological Administration’s Local Forecast (Dongne Yeobo) data. The Local Forecast system has limitations, such as systemic bias in certain regions and errors induced by complex terrain. It is often effective to approach the correction of these errors by leveraging artificial intelligence-based models. Accordingly, this research utilized the spatial pattern learning capability of CNNs to learn the spatiotemporal errors of the Local Forecast and combined it with synoptic weather observation data to improve correction accuracy. The model was trained, validated, and evaluated using precipitation data from 78 stations nationwide, covering the period from July 2021 to December 2024, with independent CNN models constructed for each prediction lead time (T=1 to 24). As a result, the proposed model demonstrated performance improvement compared to the original Local Forecast, achieving an average reduction of 16.5% in Root Mean Squared Error and an average increase of 53.9% in the Correlation Coefficient. Notably, the prediction accuracy was significantly improved in the short lead-time range of T < 6. Furthermore, even during extreme precipitation events (exceeding 50 mm in 1 hour and 90 mm in 3 hours), the CNN-based multi-point short-term precipitation correction model showed results closer to the observed values than the original forecast. A comparison with the traditional statistical correction method, Quantile Mapping, also showed that the CNN-based multi-point short-term precipitation correction model exhibited consistent superiority across all prediction lead-time intervals, confirming the effectiveness of CNN-based correction in comprehensively learning spatial information. The results of this study are expected to enhance the reliability of short-term forecasts, which can be utilized for disaster response and water resource management.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 기상청의 동네예보 자료를 대상으로 합성곱 신경망(Convolutional Neural Network, CNN)을 활용하여 단기 강수 예측 정보 보정 기법을 개발하였다. 동네예보는 복잡한 지형과 일부 지역에서 구조적 편향(Systemic bias)이 발생하는 한계가 있어, 이를 보정하기 위해 인공지능을 활용하는 방식으로 접근하는 것이 효과적일 수 있다. 이에 본 연구에서는 CNN의 공간 패턴 학습 능력을 이용하여 동네예보의 시공간적 오차를 학습하고, 종관기상관측 자료를 결합하여 보정 정확도를 향상시켰다. 모델은 2021년 7월부터 2024년 12월까지의 전국 78개 지점 강수 자료를 이용하여 예측 리드타임별(T=1~24) 독립 모델을 구성하여 학습 및 검증, 평가하였다. 그 결과, 제안된 모델은 원 동네예보 대비 평균 제곱근 오차를 평균 16.5% 감소시키고, 상관계수를 평균53.9% 향상시켰으며, 특히 리드타임 T<6 구간에서의 예측 정확도를 크게 개선시켰다. 또한 극한 강수(1시간 50 mm 이상, 3시간 90 mm 이상) 상황에서도 본 연구의 CNN 기반 다지점 단기강수예측 정보 보정 모델이 원 예보보다 관측값에 더 근접한 결과를 보였다. 전통적 통계 보정기법인 Quantile Mapping과의 비교에서도 CNN 기반 다지점 단기강수예측 정보 보정 모델이 전 예측시간 구간에서 일관된 우수성을 나타내어, 공간 정보를 통합적으로 학습하는 CNN기반 보정의 효용성을 확인하였다. 본 연구의 결과는 단기 예보의 신뢰성을 향상시켜 재해 대응 및 수자원 관리에 기여할 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
Convolutional Neural Network-Based Weather Forecasting Post-Processing Method Using Short-Term Neighborhood Forecast Data
-
Original Article

-
3D CFD Analysis of Slug Flow Frequency in Liquid-Gas Two-Phase Flow
슬러그 흐름 및 빈도 특성 분석을 위한 액체-기체 2상 흐름 3차원 수치모의
-
YongJun Kwon, Hyung-Suk Kim
권용준, 김형석
- There is a need for numerical model to evaluate and reflect the unsteady characteristics of two-phase flow in the design of underground …
지하방수로에서 발생하는 2상(two-phase) 유동의 비정상적 거동을 예측하고 이를 설계에 반영하기 위한 기술이 필요하다. 본 연구는 3차원 2상 유동해석이 가능한 OpenFOAM의 interFoam 솔버를 …
- There is a need for numerical model to evaluate and reflect the unsteady characteristics of two-phase flow in the design of underground stormwater tunnels. In this study, the interFoam solver in OpenFOAM, capable of three-dimensional two-phase flow analysis, was employed to simulate slug flow and perform a quantitative evaluation of its characteristics. Numerical simulations were conducted under various flow conditions defined by different superficial Reynolds numbers. The results demonstrated that the process of slug formation and development could be reproduced through detailed analysis of slug generation frequency, spatial occurrence, and propagation behavior. For both ReSG=1,377 and ReSG=4,320, the total number of slugs generally increased with higher ReSL values. At ReSG=4,320, slug generation was concentrated during the initial inflow stage. The slug frequency tended to increase with ReSL at ReSG=1,377, whereas at ReSG=4,320, it showed a temporary increase near the inlet but decreased along the downstream direction. The dimensionless slug frequency increased as ReSG rose from 1,377 to 4,320 under ReSL=7,070 and 12,730, whereas no distinct trend was observed with respect to ReSG when ReSL=16,500. The Strouhal number showed some deviations from the experimental results when ReSG≥4,000, but exhibited good agreement with previous experiments when ReSG≤1,377. The three-dimensional numerical model used in this study is expected to be capable of predicting the behavior of complex slug flow.
- COLLAPSE
지하방수로에서 발생하는 2상(two-phase) 유동의 비정상적 거동을 예측하고 이를 설계에 반영하기 위한 기술이 필요하다. 본 연구는 3차원 2상 유동해석이 가능한 OpenFOAM의 interFoam 솔버를 활용하여 슬러그 흐름을 모의하고 그 특성에 대한 정량적 분석을 수행하였다. 다양한 겉보기 레이놀즈수(Superficial Reynolds number)에 따라 총 12가지 유동 조건에서 수치모의를 수행하였으며, 그 결과 슬러그 형성과 이동 과정 및 발생 횟수와 위치 분석을 통해 슬러그 발달 과정을 재현할 수 있음을 확인하였다. 슬러그 발생 횟수는 ReSG=1,377 및 4,320의 경우 ReSL이 증가함에 따라 전반적으로 많아지는 경향이 나타났으며, ReSG=4,320일 때 유입 초기에 슬러그 발생 횟수가 집중되는 것으로 모의되었다. 슬러그 빈도는 ReSG=1,377인 경우 ReSL이 커지면서 증가하는 경향을 보였으나, ReSG=4,320인 경우 ReSL이 커지면서 유입부에서 일시적으로 증가하였지만 하류로 갈수록 감소하였다. 무차원 슬러그 빈도는 ReSL=7,070과 12,730인 경우 ReSG=1,377에서 4,320으로 커질 때 증가하는 것으로 나타났으나, ReSL=16,500인 경우에는 ReSG 조건에 따라 특정 경향성이 확인되지 않았다. Strouhal number는 ReSG≥4,000인 조건에서 수리실험과 다소 차이가 발생하였으나, ReSG≤1,377인 조건에서 기존 수리실험 결과와 잘 일치하는 것으로 나타났다. 본 연구의 3차원 수치모의를 활용하여 복잡한 슬러그 흐름에 대한 거동을 예측할 수 있는 것으로 판단된다.
-
3D CFD Analysis of Slug Flow Frequency in Liquid-Gas Two-Phase Flow
-
Original Article
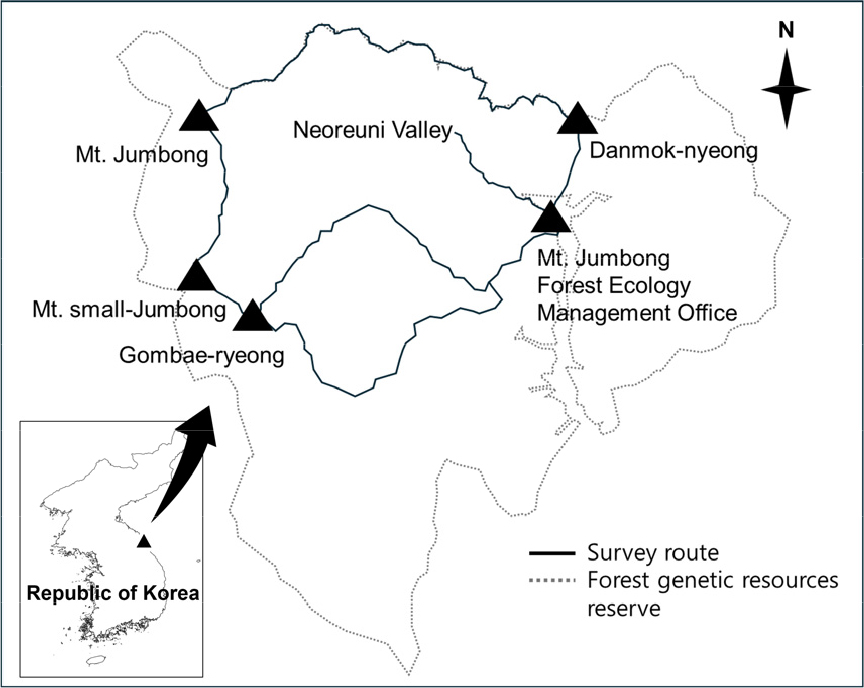
-
Dietary Analysis of Hydropotes inermis argyropus in Mt. Jumbong, using Fecal Samples
배설물 시료를 이용한 점봉산 서식 고라니의 먹이원 분석 연구
-
So-yeon Kwon, Sungbae Joo, Jeongsoo Park
권소연, 주성배, 박정수
- The water deer (Hydropotes inermis) in family Cervidae is endangered species, listed as “vulnerable” by the International Union for Conservation …
고라니(Hydropotes inermis)는 국제자연보전연맹(IUCN) 적색목록에 멸종위기 취약종으로 등재된 사슴과 포유류로, 중국과 한국에 주로 분포한다. 중국 개체군은 서식지 파편화와 밀렵으로 인해 분포가 …
- The water deer (Hydropotes inermis) in family Cervidae is endangered species, listed as “vulnerable” by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). Its native distribution is limited to few areas in China and Korean peninsula. While Chinese population has undergone severe decline due to habitat fragmentation and poaching, the Korean population is managed as vermin because of the crop damage associated with its high population density. Here, we applied NGS metabarcoding to elucidate possible food sources of the species inhabiting Mt. Jumbong. Fecal samples were collected at two-month intervals from April to October to assess seasonal variation in diet. As a result, total of 283,362 reads were obtained from 22 fecal samples collected between April and August, yielding 582 amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) for the downstream analyses. The genera Quercus, Carpinus, and Acer were selected as the major food source of water deer inhabiting Mt. Jumbong, with high relative read abundance and frequency of occurrence. Our findings provide baseline data for understanding the feeding ecology of mountain-dwelling water deer and to contribute to long-term monitoring of plant community shifts and herbivore–plant interactions under climate change.
- COLLAPSE
고라니(Hydropotes inermis)는 국제자연보전연맹(IUCN) 적색목록에 멸종위기 취약종으로 등재된 사슴과 포유류로, 중국과 한국에 주로 분포한다. 중국 개체군은 서식지 파편화와 밀렵으로 인해 분포가 크게 축소되었으나, 한국 개체군은 한반도 전역에서 높은 밀도로 분포하며 농작물 피해를 일으켜 유해야생동물로 관리되고 있다. 본 연구에서는 자연성이 높고 장기생태연구가 수행되고 있는 점봉산 일대에서 고라니 배설물을 채집하여 NGS 기반 메타바코딩 분석을 실시하였다. 샘플링은 4월부터 10월까지 두 달 간격으로 진행되었으며 선조사법에 따라 정해진 경로 상에서 배설물을 채집하였다. 그 결과 4월부터 8월까지 총 22개의 배설물을 채집하였으며 전체 시료에서 283,362개의 read수, 총 582개의 ASV (amplicon sequence variant)를 확보하여 분석에 사용하였다. 점봉산 서식 고라니의 먹이원의 비율과 출현 빈도를 비교한 결과 비율과 빈도가 모두 높았던 단풍나무속, 서어나무속, 참나무속을 점봉산 고라니의 주요 먹이원으로 추정하였다. 본 연구는 산간 지역 고라니의 먹이원에 대한 기초 자료를 제공하고 있으며, 장기적인 측면에서 기후변화에 따른 식물 군집 변화와 고라니의 먹이원 변화를 모니터링할 수 있는 기반 자료로 활용될 수 있을 것이라 기대한다.
-
Dietary Analysis of Hydropotes inermis argyropus in Mt. Jumbong, using Fecal Samples
-
Original Article

-
Analysis on Grain-Size-Dependent Mobility of Gravel Bed Materials in Large-Scale Experimental Flow Conditions
실규모 실험 흐름 조건에서의 자갈 하상 입경별 이동성 분석 연구
-
Eunkyung Jang, Woochul Kang, Jaeho Kim, Un Ji
장은경, 강우철, 김재호, 지운
- This study is an experimental investigation to determine the grain-size dependent mobility of gravel-bed materials under full-scale flow conditions. Experiments were conducted …
본 연구는 실규모 실험 흐름 조건에서 자갈하상 재료의 입경별 이동성을 규명하기 위한 실험적 연구이다. 한국건설기술연구원 안동하천실험센터의 실규모 수로에서 두 가지 수리 조건(Case …
- This study is an experimental investigation to determine the grain-size dependent mobility of gravel-bed materials under full-scale flow conditions. Experiments were conducted at the full-scale flume of the Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology's Andong River Experiment Center under two hydraulic conditions (Case 1: gate 50% open, discharge 2.683 m3/s, water depth 0.753 m, energy slope 0.00284; Case 2: gate fully open, discharge 2.723 m3/s, water depth 0.752 m, energy slope 0.00286). Gravel particles ranging from 2 to 15 mm were arranged in a specific section to analyze the variation of dimensionless shear stress (
τ
*
) with grain size. The experimental results showed that dimensionless shear stress decreased nonlinearly with increasing grain size, and critical values (
τ
c
*
) marking the transition between motion and non-motion were identified in the 8-10 mm range for Case 1 and in the 12-15 mm range for Case 2. The calculated critical values were approximately three times higher than the conventional Shields criterion (0.04-0.05), which is interpreted as a combined result of turbulence scale expansion, inter-particle interlocking, and high Reynolds number conditions acting in combination. The results of this study provide experimental evidence for full-scale calibration of the Shields diagram and can be utilized as fundamental data for improving the accuracy of bed stability assessment and sediment transport prediction models in gravel-bed rivers.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 실규모 실험 흐름 조건에서 자갈하상 재료의 입경별 이동성을 규명하기 위한 실험적 연구이다. 한국건설기술연구원 안동하천실험센터의 실규모 수로에서 두 가지 수리 조건(Case 1: 게이트 50% 개방, 유량 2.683 m3/s, 수심 0.753 m, 에너지 경사 0.00284; Case 2: 게이트 완전 개방, 유량 2.723 m3/s, 수심 0.752 m, 에너지 경사 0.00286)에서 실험을 수행하였으며, 2~15 mm 범위의 자갈을 일정 구간에 배열하여 입경에 따른 무차원 전단응력( τ * )의 변화를 분석하였다. 실험 결과, 무차원 전단응력은 입경 증가에 따라 비선형적으로 감소하였으며, Case 1은 8~10 mm, Case 2는 12~15 mm 조건에서 이동과 비이동이 전이되는 한계값( τ c * )이 확인되었다. 기존 Shields 도표의 기준값(0.04~0.05)보다 약 3배 높은 한계값이 산정되었으며 이는 난류 스케일 확장, 입자 간 결속, 높은 Reynolds 수 등이 복합적으로 작용한 결과로 해석된다. 본 연구 결과는 Shields 곡선의 실규모 보정에 대한 실험적 근거를 제공하며, 자갈하천의 하상 안정성 평가 및 유사이송 예측 모델의 정확도 향상에 기초자료로 활용될 수 있다.
-
Analysis on Grain-Size-Dependent Mobility of Gravel Bed Materials in Large-Scale Experimental Flow Conditions
-
Original Article
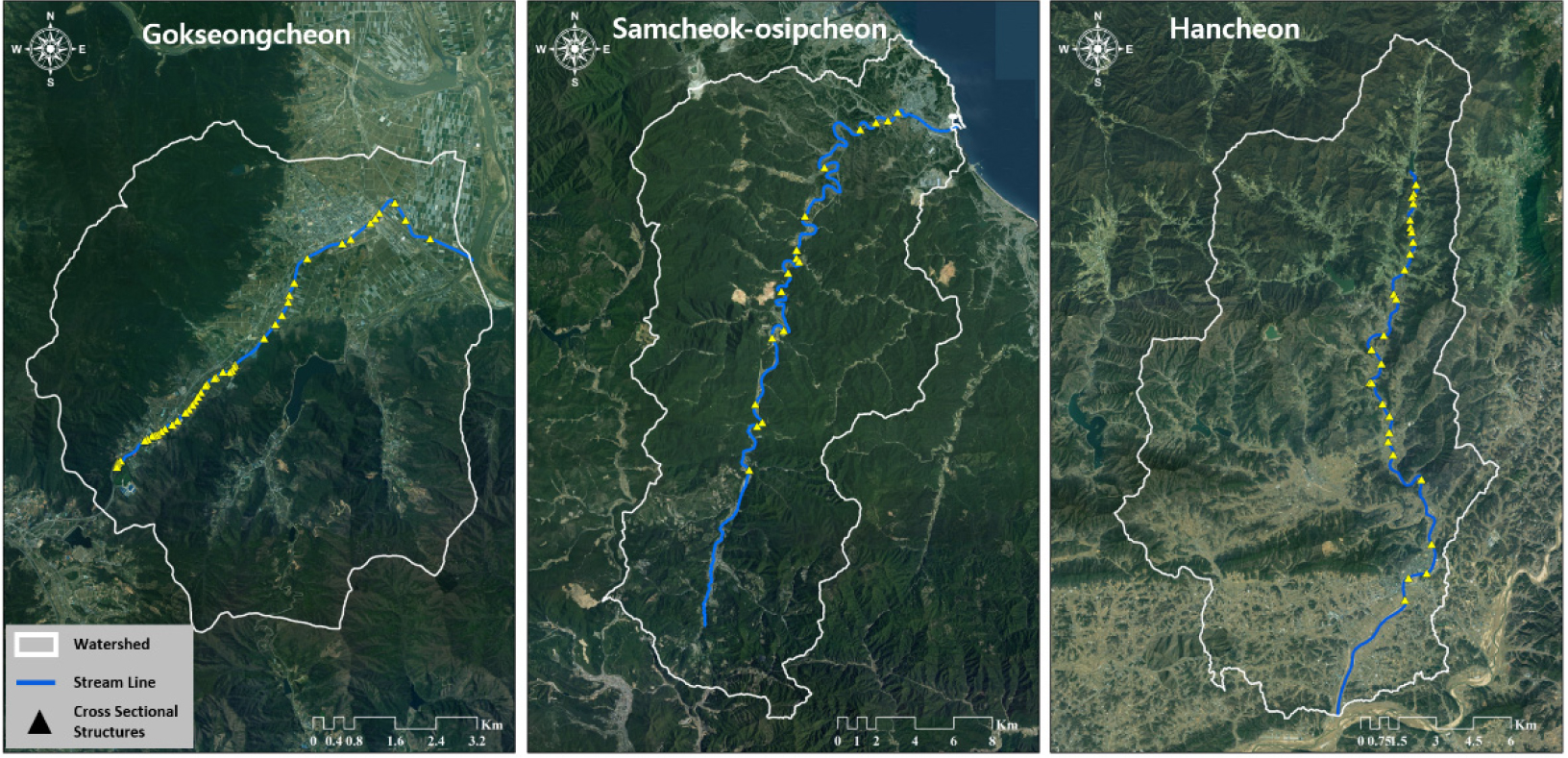
-
A Study on the Quantitative Comparative Assessment of Structural and Functional River Connectivity
하천의 구조적 연결성과 기능적 연결성의 정량적 비교 평가 연구
-
Hong Il, Hyoung Sub Sin, Joon Gu Kang, Hong Koo Yeo, Dong Ho Nam
홍일, 신형섭, 강준구, 여홍구, 남동호
- This study proposes a new methodology for the quantitative assessment of longitudinal river connectivity. Current assessments in Korea rely on qualitative grades …
본 연구는 하천의 종적 연결성을 정량적으로 평가하기 위한 새로운 방법론을 제시한다. 현행 국내 하천 연속성 평가는 ‘연속’, ‘훼손’, ‘단절’의 정성적 등급을 사용하며, …
- This study proposes a new methodology for the quantitative assessment of longitudinal river connectivity. Current assessments in Korea rely on qualitative grades (Continuous, Damaged, Disconnected), which limit quantitative comparison as most rivers are classified as ’Disconnected’ based on the lowermost barrier. Furthermore, while the existing Dendritic Connectivity Index (DCI) reflects network structure, it assumes all barriers cause complete disconnection, thereby failing to capture actual ecological functions. To address these limitations, this study proposes a new functional connectivity index, DCIm, which integrates field-measured “fish passage rates (%)“ from Korean guidelines into the DCI framework. The DCIm index is calculated using the cumulative product of passability rates for all downstream barriers, establishing the theoretical relationship DCIm≤DCI (functional connectivity≤structural connectivity). When applied to three Korean rivers (Gokseongcheon, Samcheok-osipcheon, and Hancheon), the structural DCI was 3.53%~9.80%. However, the actual functional connectivity (DCIm) was significantly lower (0.53%~4.43%), resulting from the presence of barriers with low or zero fish passage rates (i.e., functional disconnection). This study defines the difference between DCI (structural potential) and DCIm (actual function) as the “functional limitation“ caused by barrier inefficiency, providing an analytical framework for its quantification. The proposed index complements the current qualitative assessment by offering a quantitative scale and serves as an evaluation tool to separately analyze the effects of barrier removal versus barrier enhancement (i.e., improving passability). This framework is expected to contribute to more rational priority setting in river restoration and management planning.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 하천의 종적 연결성을 정량적으로 평가하기 위한 새로운 방법론을 제시한다. 현행 국내 하천 연속성 평가는 ‘연속’, ‘훼손’, ‘단절’의 정성적 등급을 사용하며, 하류의 횡단구조물 상태에 따라 대부분의 하천이 단절(또는 훼손)로 평가되는 등 정량적 비교에 한계가 있다. 또한 기존 DCI 지표는 하천망의 구조적 특성은 반영하지만, 모든 구조물이 완전한 단절 상태로 가정되어 실제 생태학적 기능을 충분히 반영하지 못한다. 이러한 한계를 보완하기 위해, 본 연구에서는 DCI의 평가 틀에 국내 지침의 실측 자료인 어류 이동률(%)을 통합하여 새로운 기능적 연결성 지표인 DCIm을 제안하였다. DCIm은 하류측 모든 구조물의 통과율을 누적하여 곱하는 방식을 적용함으로써, DCIm≤DCI(기능적 연결성≤ 구조적 연결성)라는 관계가 성립된다. 개발된 지표를 곡성천, 삼척오십천, 한천에 적용한 결과, 횡단구조물 설치로 인한 DCI는 3.53%~9.80% 범위로 나타났다. 그러나 어류 이동률이 낮거나 0%인 구조물(기능적 단절)이 존재함에 따라, 실제 기능적 연결성(DCIm)은 0.53%~4.43% 범위로 DCI보다 더욱 낮게 산정되었다. 본 연구는 DCI(구조적 잠재력)와 DCIm(실제 기능)의 차이를 구조물 기능 저하로 인한 기능적 제약으로 해석하고, 이를 정량적으로 평가하는 분석틀을 제시하였다. 제안된 지표는 현행 등급제 평가의 정량적 한계를 보완하며, 구조물 제거와 구조물 기능 개선의 효과를 분리하여 검토할 수 있는 평가방법으로 활용 가능하다. 이를 통해 하천복원 및 관리계획의 합리적 우선순위 설정에 기여할 수 있을 것으로 판단된다.
-
A Study on the Quantitative Comparative Assessment of Structural and Functional River Connectivity
-
Original Article
-
Development of a Methodology for Calculating Rainfall Thresholds to Establish Warning Criteria for River Impact Based Forecast
하천 영향예보 발령기준 설정을 위한 영향한계강우량 산정기법 개발
-
Youngseok Song, Hyoungsub Shin, Byungsik Kim, Yoonkyung Park
송영석, 신형섭, 김병식, 박윤경
- This study developed an analytical method for determining the warning criteria of river impact based forecasts capable of early prediction of flood …
본 연구에서는 하천을 대상으로 침수피해를 조기에 예측할 수 있는 하천 영향예보 발령기준의 분석방법을 개발하고 강원도 지역을 대상으로 분석하였다. 지속시간 3시간에 대한 영향한계강우량을 …
- This study developed an analytical method for determining the warning criteria of river impact based forecasts capable of early prediction of flood damage targeting rivers, and applied it to the Gangwon Province region. The rainfall threshold for a 3-hour duration was calculated, and stage-based impact based forecast issuance criteria were proposed, linking the river's design frequency and planned flood level. Analysis results showed that the rainfall threshold, considering the design frequency of rivers located in Gangwon Province, ranged from 114 mm to 232 mm and increased nonlinearly as the design frequency increased. Relatively higher rainfall threshold amounts were calculated for the east coast and mountainous terrain areas. Furthermore, for the four-stage impact based forecast issuance criteria, the rainfall threshold for a 3-hour duration was analyzed as follows: Concern (24 mm ~ 35 mm), Caution (39 mm ~ 58 mm), Warning (61 mm ~ 79 mm), and Severe (97 mm ~ 129 mm). The results of this study strategically propose impact based forecast issuance criteria for rivers by considering rainfall-runoff-water level relationships. This confirms the feasibility of an impact based forecast system that incorporates hydrological and topographical characteristics, moving beyond rainfall-centric heavy rain forecasts. Future research comparing and validating these findings against actual flood damage cases is expected to enhance the reliability of the analytical methods and enable standardization of impact based forecast criteria
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 하천을 대상으로 침수피해를 조기에 예측할 수 있는 하천 영향예보 발령기준의 분석방법을 개발하고 강원도 지역을 대상으로 분석하였다. 지속시간 3시간에 대한 영향한계강우량을 산정하고 하천의 설계빈도와 계획홍수위를 연계한 단계별 영향예보 발령기준을 제시하였다. 분석결과 강원도에 위치한 하천의 설계빈도를 고려한 영향한계강우량은 114 mm ~ 232 mm의 범위가 분석되었으며 설계빈도가 증가할수록 비선형적으로 증가하였다. 동해안 및 산악지형 지역에서 영향 한계강우량이 상대적으로 높게 산정되다. 또한, 영향예보의 4단계 발령기준에 대하여 지속시간 3시간의 영향한계강우량을 관심, 24 mm ~ 35 mm, 주의 39 mm ~ 58 mm, 경계 61 mm, ~ 79 mm, 심각 97 mm ~ 129 mm이 분석되었다. 본 연구의 결과는 강우-유출-수위를 고려하여 하천의 영향예보의 발령기준을 정략적으로 제시함으로써 강우량 중심의 호우예보에서 수문학적 및 지형적 특성을 고려한 영향예보 체계의 가능성을 확인하였다. 향후 연구에서 실제 침수피해 사례와 비교 검증한다면 분석방법에 대한 신뢰성 향상과 영향예보의 기준 표준화가 가능할 것으로 예상된다.
-
Development of a Methodology for Calculating Rainfall Thresholds to Establish Warning Criteria for River Impact Based Forecast
-
Original Article
-
Analysis of Environmental Impact Assessment Trends in Korea’s Renewable Energy (Solar and Wind) Development Projects: Focusing on 2008–2024
한국 재생에너지(태양광·풍력) 개발사업의 환경영향평가 동향 분석: 2008~2024년을 중심으로
-
Hyohyemi Lee, Kang-Hyun Cho
이효혜미, 조강현
- This study analysed the temporal and spatial performance of the environmental impact assessment system for solar and wind power generation projects implemented …
본 연구는 2008년부터 2024년까지 한국에서 시행된 태양광 및 풍력 발전 사업의 환경영향평가 제도 운영 실적을 시간적·공간적으로 분석하였다. 환경부 환경영향평가 정보지원시스템(EIASS) 자료를 기반으로 …
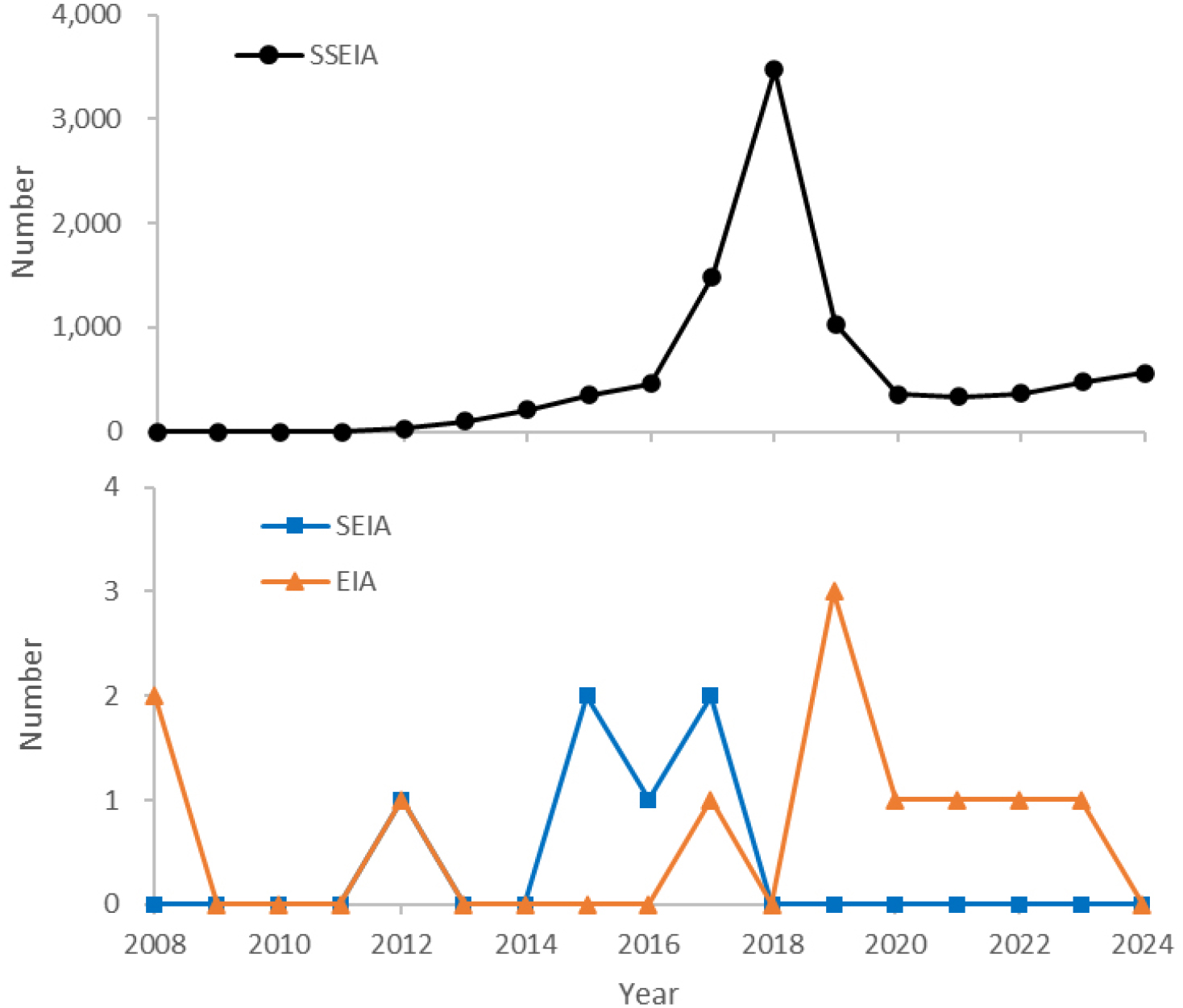
- This study analysed the temporal and spatial performance of the environmental impact assessment system for solar and wind power generation projects implemented in Korea between 2008 and 2024. Using data from the Ministry of Environment’s Environmental Impact Assessment Information Support System (EIASS), the study provided a comprehensive review of Strategic Environmental Impact Assessments (SEIAs), Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) and Small-Scale Environmental Impact Assessments (SSEIAs). The study also analysed the correlation with trends in power generation growth using renewable energy deployment statistics from the Korea Energy Agency. The analysis revealed that, during the study period, the number of solar power assessments was 9,272, which was over 48 times higher than the number of wind power assessments (195 cases). A structural bias was confirmed, with 98% of solar power assessments concentrated in small-scale environmental impact assessments. The number of solar power assessments increased sharply in 2018 before declining due to strengthened regulations. Although there were fewer wind power projects in total, they showed a relatively higher proportion of SEIAs and EIAs. Solar power projects were excessively concentrated regionally in the Honam region (Yeongsan River Basin Environmental Office and Jeonbuk Regional Environmental Office), whereas wind power projects tended to be concentrated at the Ministry of Environment headquarters and the Daegu and Wonju Regional Environmental Offices. These results reflect the impact of policy changes, including the ‘Renewable Energy 3020’ policy, strengthened cumulative development and separation regulations, and the establishment of a dedicated wind power team. Suggested policy implications include: Preventing haphazard development and ’fragmentation’ of small-scale projects and introducing cumulative impact assessments; Shifting to an induced-location policy that considers regional imbalance mitigation and establishing a planned-location system for wind power, as well as strengthening dedicated management. This study empirically demonstrates the necessity of shifting renewable energy policy towards a spatial approach that considers environmental sustainability, grid integration capacity and local acceptance. This approach moves beyond a focus solely on quantitative expansion.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 2008년부터 2024년까지 한국에서 시행된 태양광 및 풍력 발전 사업의 환경영향평가 제도 운영 실적을 시간적·공간적으로 분석하였다. 환경부 환경영향평가 정보지원시스템(EIASS) 자료를 기반으로 전략환경영향평가, 환경영향평가, 소규모환경영향평가를 통합적으로 검토하고, 한국에너지공단의 재생에너지 보급통계를 활용하여 발전량 증가 추이와의 연계성을 분석하였다. 분석 결과, 조사기간 동안 태양광 발전 평가 건수는 9,272건으로 풍력 발전(195건)에 비해 48배 이상 많았으며, 특히 태양광 발전의 98%가 소규모환경영향평가에 집중되는 구조적 편중이 확인되었다. 태양광의 평가 건수는 2018년에 급격히 증가한 후 규제 강화로 감소하였고, 풍력은 총량은 적으나 전략환경영향평가와 환경영향평가의 비중이 상대적으로 높았다. 지역적으로는 태양광 사업이 호남권(영산강유역환경청 및 전북지방환경청)에 과도하게 편중되었으며, 풍력은 환경부 본부와 대구·원주지방환경청에 집중되는 경향을 보였다. 이러한 결과는 ‘재생에너지 3020’ 정책, 누적 개발·이격 규제 강화, 풍력 전담팀 신설 등 정책 변화의 영향을 반영한다. 정책적 함의로서, 소규모 개발의 난개발·‘쪼개기’ 방지 및 누적영향평가 도입, 지역적 편중 완화를 고려한 유도형 입지 정책 전환, 풍력 발전의 계획입지제 정착 및 전담 관리 강화 등이 제시되었다. 본 연구는 재생에너지 개발의 양적 확대 중심에서 벗어나 환경성·계통수용성·지역수용성을 고려한 공간 기반 재생에너지 정책 전환의 필요성을 실증적으로 제시한다.
-
Analysis of Environmental Impact Assessment Trends in Korea’s Renewable Energy (Solar and Wind) Development Projects: Focusing on 2008–2024
-
Original Article
-
Evaluation of Ecosystem Services in Constructed Bird Habitats Within Waterfront Zones: A Case Study of the Busan Eco Delta City Project
친수구역 내 철새서식처 조성지의 생태계 서비스 평가: 부산 에코델타시티 사업을 중심으로
-
Chi Ho Song, Gwon Soo Bahn
송치호, 반권수
- This study aims to develop ecosystem service assessment indicators for the planned migratory bird habitat within the waterfront zone of the Busan …
본 연구는 부산 에코델타시티(EDC) 친수구역 사업 내 조성 예정인 철새서식처를 대상으로 생태계서비스 평가지표를 개발하고, 조성 전·후 변화를 정량적으로 예측, 평가하는 것을 목적으로 …
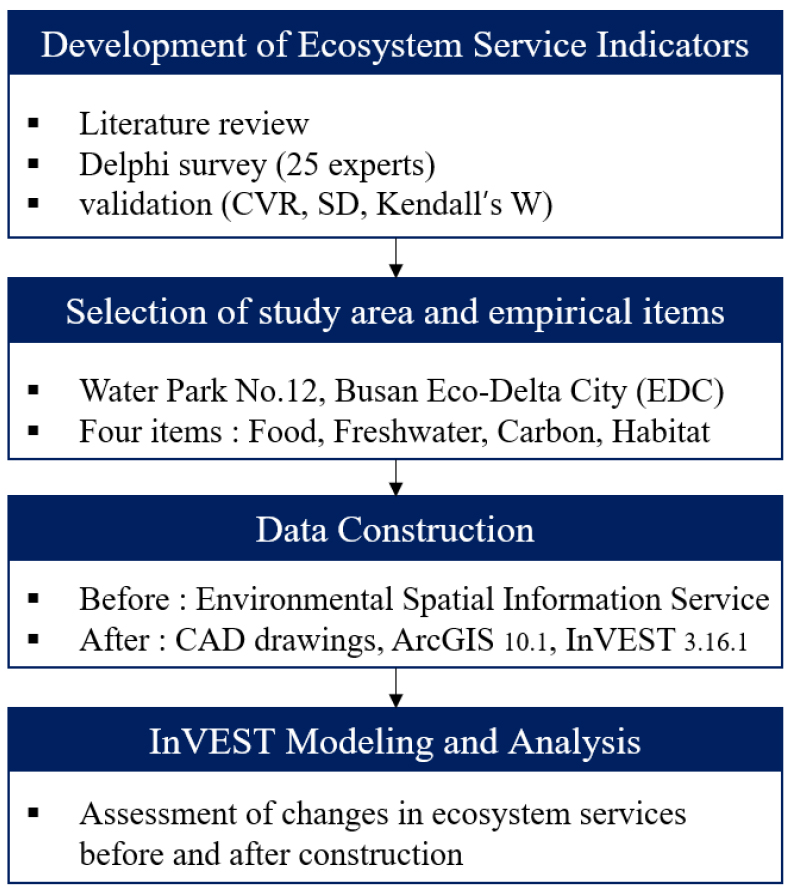
- This study aims to develop ecosystem service assessment indicators for the planned migratory bird habitat within the waterfront zone of the Busan Eco Delta City (EDC) project and to quantitatively predict and evaluate changes before and after habitat construction. Candidate indicators were first derived from domestic and international wetland-related studies and the classification frameworks of the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MA), The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity (TEEB), and the National Institute of Ecology (NIE). A Delphi survey was conducted to finalize nine assessment indicators: ‘food provision’ and ‘water resources’ for provisioning services; ‘air purification’ and ‘carbon storage’ for regulating services; ‘habitat’ and ‘biodiversity’ for supporting services; and ‘ecotourism’, ‘environmental education’, and ‘cultural identity’ for cultural services. Empirical analyses were performed using GIS-based InVEST models on four indicators—food production, carbon storage, water yield, and habitat quality—selected through expert consensus. The results showed substantial improvements across all evaluated ecosystem services: total food production increased from 27 t to 72 t, average water yield from 733.05 mm to 906.83 mm, and average carbon storage from 30.4 t C/ha to 54.3 t C/ha. The maximum habitat quality index also improved from 0.8 to 0.9, indicating qualitative enhancement of habitat conditions. These findings demonstrate that the creation of a migratory bird habitat can positively contribute to ecosystem service functions within an urban development area. The assessment indicators proposed in this study provide a foundational framework for evaluating urban bird habitats by integrating expert consensus with spatially explicit InVEST modeling, offering valuable baseline data for future habitat restoration and waterfront ecological planning.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 부산 에코델타시티(EDC) 친수구역 사업 내 조성 예정인 철새서식처를 대상으로 생태계서비스 평가지표를 개발하고, 조성 전·후 변화를 정량적으로 예측, 평가하는 것을 목적으로 한다. 국내외 습지 관련 선행연구와 MA, TEEB, 국립생태원 분류체계를 기반으로 후보항목을 선정하였으며, 델파이 분석을 통해 공급서비스는 ‘식량’, ‘수자원’, 조절서비스는 ‘대기정화’, ‘탄소저장’, 지지서비스는 ‘서식처’, ‘생물다양성’, 문화서비스는 ‘생태관광’, ‘생태교육’, ‘문화적 정체성’ 등 총 9개 평가항목을 도출하였다. 실증분석은 전문가 합의를 통해 도출된 먹이생산량, 탄소저장, 담수공급량, 서식처 질 등 4개 지표에 대해 GIS 기반 InVEST 모델을 활용하여 수행하였다. 분석 결과, 총 먹이생산량은 27 t에서 72 t으로, 평균 담수공급량은 733.05 mm에서 906.83 mm로, 평균 탄소저장량도 30.4 t C/ha에서 54.3 t C/ha로 증가하는 것으로 나타났다. 서식처 질 지수의 최대값은 0.8에서 0.9로 상승하여 서식환경의 질적 개선이 확인되었다. 이러한 결과는 철새서식처 조성이 도시개발 사업지역 내 생태계서비스 기능에 긍정적으로 기여함을 보여주며, 본 연구에서 제시한 평가지표는 InVEST 기반 공간분석과 전문가 합의를 결합한 도시 철새서식처 평가의 선구적 기초자료로 활용될 수 있다.
-
Evaluation of Ecosystem Services in Constructed Bird Habitats Within Waterfront Zones: A Case Study of the Busan Eco Delta City Project
-
Original Article
-
A Site-Specific Evaluation of Streamflow-Fish Assessment Index (FAI) Relationships for Identifying Long-Term Monitoring Sites
하천유량-어류건강성평가지수 관계를 통한 장기모니터링 지점 선정 고찰
-
Ji Youn Sung
성지연
- This study selected eight river sites from the biomonitoring network operated by the National Institute of Environmental Research (NIER), where the Fish …
본 연구는 유량 변동성과 어류 건강성간의 상관성을 분석하기 위해 국립환경과학원이 어류건강성평가지수(FAI)를 제공하는 지점 중 8개 하천 지점을 선정 후, 하천 유량 조건과 …
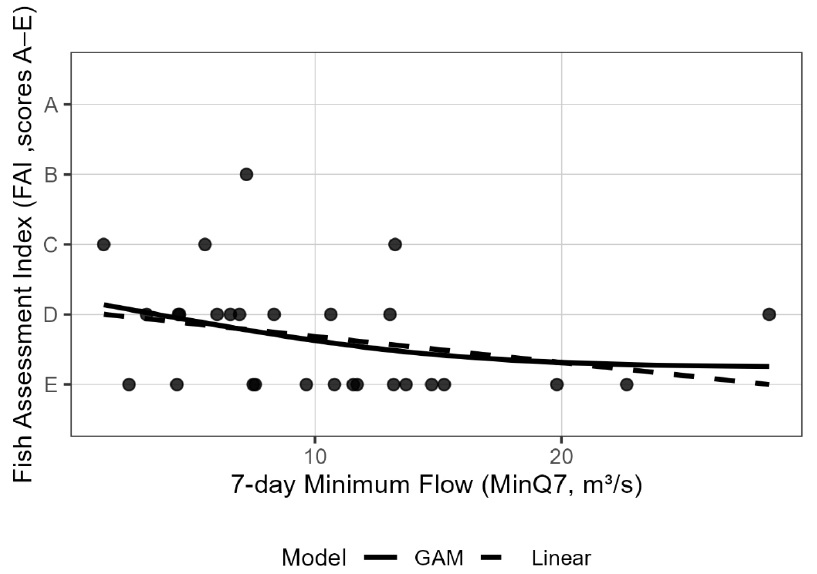
- This study selected eight river sites from the biomonitoring network operated by the National Institute of Environmental Research (NIER), where the Fish Assessment Index (FAI) is routinely measured, to analyze the relationship between streamflow conditions and FAI and to identify sites suitable for long-term biological monitoring. The 7-day minimum flow (MinQ7) was used as a representative low-flow indicator, and the correlation between flow variablilty and fish community health was examined. Although the relationship between MinQ7 and FAI was weak or statistically insignificant at most sites, a statistically significant negative correlation was identified at the Gokgyocheon-2 site. This indicates that low-flow conditions exert a more direct influence on fish assemblages at this site compared to others, suggesting its potential suitability as a representative location for future verification of ecological responses to low-flow conditions and for long-term monitoring. This study demonstrates the value of integrating hydrological characteristics into biomonitoring network analyses and provides useful baseline information for Environmental Impact Assessment that evaluate the ecological effects of flow variation. By applying a simple statistical framework, we propose a process for identifying monitoring sites suitable for long-term assessment of hydro-ecology relationships. The findings also highlight the need for further research on the impacts of anthropogenic flow variability on biological monitoring networks.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 유량 변동성과 어류 건강성간의 상관성을 분석하기 위해 국립환경과학원이 어류건강성평가지수(FAI)를 제공하는 지점 중 8개 하천 지점을 선정 후, 하천 유량 조건과 FAI간의 관계를 분석하여, 지점별 생태 반응 특성을 평가하고 장기 생물 모니터링에 적합한 지점을 도출하고자 하였다. 하천유량으로 저유량 지표인 7일 최소유량(MinQ7)을 활용하였으며, 대부분의 지점에서 하천 저유량과 FAI 간의 관계가 약하거나 통계적으로 유이하지 않은 것으로 나타났으나, 곡교천2 (Gokgyocheon-2) 지점에서는 통계적으로 유의한 음의 상관관계가 확인되어, 다른 지점에 비해 저유량 영향이 어류군집에 직접적인 영향을 보이는 것으로 나타났으며, 향후에도 저유량 생태반응 검증과 장기 모니터링을 위한 대표지점으로 활용가능성을 검토할 수 있음을 보여준다. 본 연구는 생물 측정망 모니터링에 수문 특성을 연계하여 분석하는데 의미가 있을 것으로 판단되며, 유량변화가 생태계에 미치는 영향을 평가하는 환경영향평가 단계에 유용한 기초자료를 제공한다. 본 연구는 간단한 통계적 분석 방법을 통해 수문-생태 영향 관계를 지속적으로 모니터링 할 수 있는 지점의 선정 과정을 제안하였으며, 향후 인위적인 유량 변동에 따른 생물측정망 영향에 대한 추가 연구의 필요성을 제시한다.
-
A Site-Specific Evaluation of Streamflow-Fish Assessment Index (FAI) Relationships for Identifying Long-Term Monitoring Sites
-
Original Article
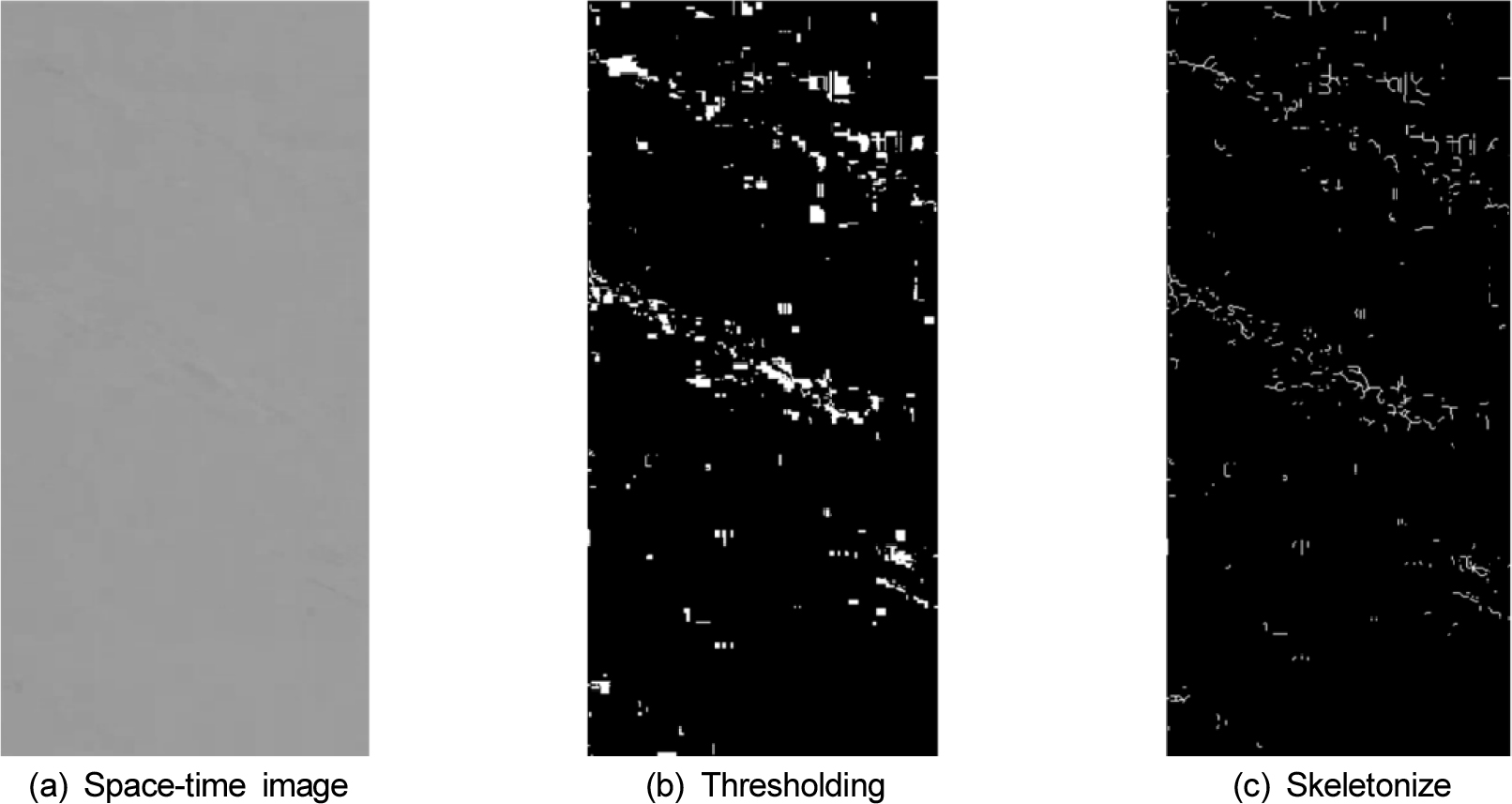
-
A Study on the Applicability of Space–Time Image Velocimetry (STIV) for Real-Time Discharge Monitoring in Irrigation Channels
농업 용수로의 실시간 유량 모니터링을 위한 STIV 적용성 연구
-
Jae-Seon Yoon, Yong-Woo Joo, Sang-Jin Hong, Jang Hyun Sung, Seojun Kim
윤재선, 주용우, 홍상진, 성장현, 김서준
- This study aimed to evaluate the field applicability of the STIV (Space-Time Image Velocimetry) system, a non-contact image velocity measurement technique, for …
본 연구에서는 농업 용수로 유량 계측의 신뢰성 있는 연속 모니터링을 위해, 비접촉식 영상 유속 측정 기법인 STIV(Space-Time Image Velocimetry)시스템의 현장 적용성을 평가하고 …
- This study aimed to evaluate the field applicability of the STIV (Space-Time Image Velocimetry) system, a non-contact image velocity measurement technique, for discharge gauging in agricultural channels and to explore standardization methods for reliable continuous monitoring. Comparative measurements were conducted both during daytime (6 runs) and nighttime (4 runs) using the STIV system and the standard equipment, ADCP (Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler), at the Eougyo agricultural channel in Wanju-gun, Jeollabuk-do. The results confirmed the technical validity of the STIV system by demonstrating high repeatability under both day and night conditions. However, the STIV-measured discharge consistently exhibited a systematic error relative to the ADCP measurements, showing an average error of 13.48% during the day and 17.78% at night. This systematic error indicates that the generic depth-averaged velocity coefficient (velocity coefficient) applied for velocity estimation overestimated the actual velocity profile of the site, suggesting that a recalibrated depth-averaged velocity coefficient around 0.75 is necessary for the Eougyo site. Furthermore, the slight increase in error rate during nighttime confirmed issues related to reduced accuracy due to illumination changes. These findings show that STIV is technically viable for measuring discharge in agricultural channels and can contribute to the future expansion of CCTV-based water resource survey systems. However, to ensure stable operation, site-specific depth-averaged velocity coefficient calibration based on ADCP measurements, the implementation of day/night dual-model correction and securing high-performance auxiliary lighting are essential follow-up tasks.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 농업 용수로 유량 계측의 신뢰성 있는 연속 모니터링을 위해, 비접촉식 영상 유속 측정 기법인 STIV(Space-Time Image Velocimetry)시스템의 현장 적용성을 평가하고 표준화 방안을 모색하고자 하였다. 전북 완주군 어우교 농업 용수로에서 STIV 시스템과 ADCP (Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler)를 이용하여 주간(6회) 및 야간(4회) 비교 측정을 수행하였다. 측정 결과, STIV 시스템은 주간 및 야간 환경 모두에서 높은 정밀도를 확보하며 기술적 유효성을 입증하였다. STIV 유량은 ADCP 실측값 대비 주간 평균 13.48%, 야간 평균 17.78%의 차이가 나타났는데 이는 유속 산정 시 적용된 평균유속 환산계수가 해당 현장의 연직 유속 분포를 과대평가 했음을 의미하며, 실제 어우교 현장과 같이 수심이 낮은 하천의 경우 바닥 영향이 크기 때문에 평균유속 환산계수는 0.75 정도를 적용하여 유량을 재산정할 필요가 있음을 확인하였다. 또한, 야간 측정 시 오차율이 주간 대비 소폭 증가하는 경향을 보여 조도 변화에 따른 정확도 저하 문제를 확인하였다. 이 연구 결과는 STIV가 농업 용수로 유량 측정에 기술적으로 유효하며, 향후 CCTV 기반의 수자원 조사 체계 확산에 기여할 수 있음을 보여준다. 다만, 정확도 높은 자동유량조사를 위해서는 실측 기반의 현장 특화 평균유속 환산계수 검보정 및 주야간 이원화된 보정 모델 구축 및 보조 광원 확보가 필수적이겠다.
-
A Study on the Applicability of Space–Time Image Velocimetry (STIV) for Real-Time Discharge Monitoring in Irrigation Channels
-
Original Article
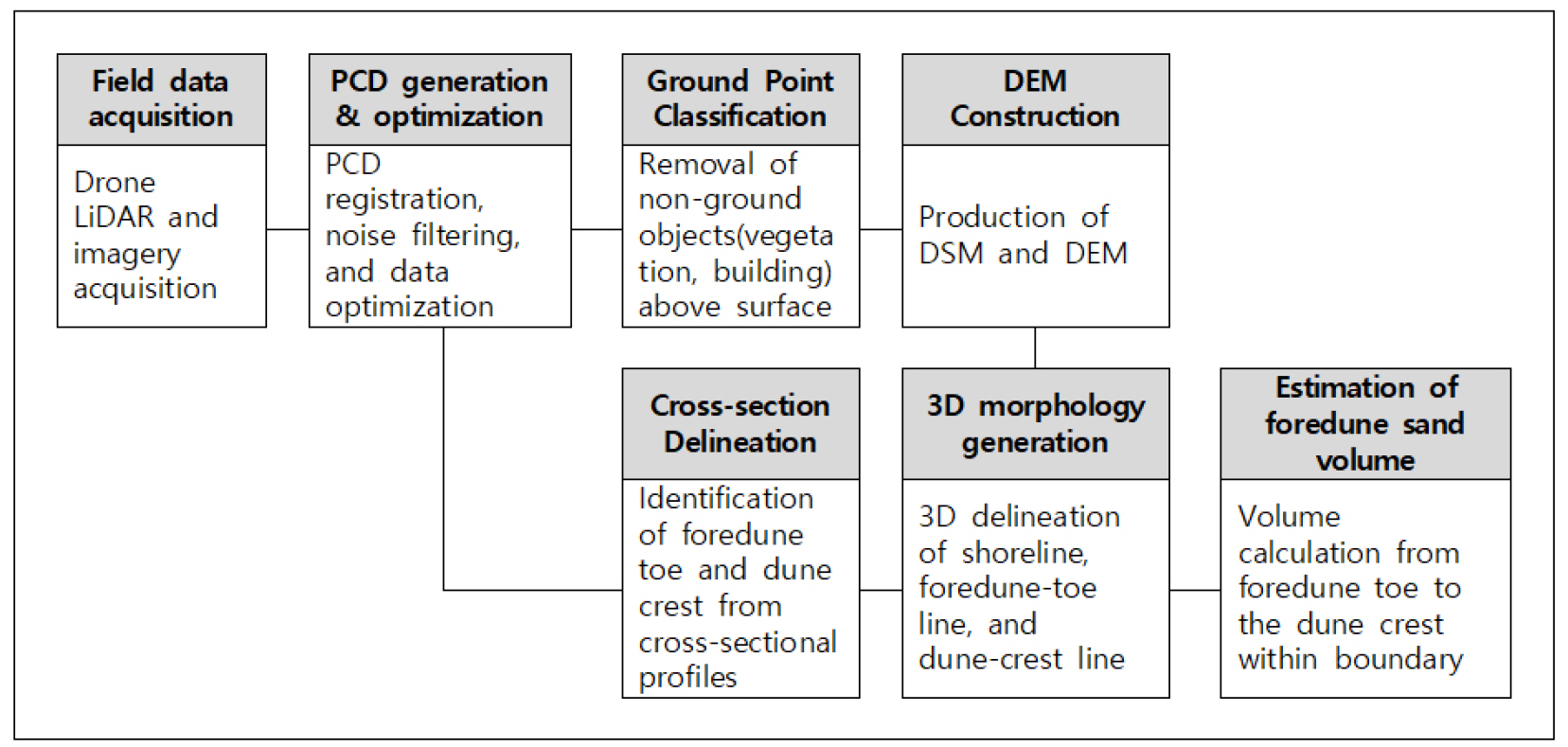
-
Three-Dimensional Estimation of Foredune Sand Volume in Coastal Dunes Using Drone LiDAR
드론 라이다를 활용한 해안사구 전사구 모래량의 3차원 체적 산정 연구
-
Giyoung Ock, Tae-Heon Kim
옥기영, 김태헌
- Coastal sand dunes provide important ecosystem services, serving as natural breakwaters and maintaining biodiversity. The sand volume of foredunes is a key …
해안사구는 자연방파제 역할과 생물다양성 유지 등 중요한 생태계 서비스를 제공하며, 이러한 기능의 핵심 요소는 전사구의 모래량이다. 우리나라에서는 전사구 모래량을 해안사구의 역동성과 규모를 …
- Coastal sand dunes provide important ecosystem services, serving as natural breakwaters and maintaining biodiversity. The sand volume of foredunes is a key factor in sustaining these functions. In Korea, foredune sand volume is used as a core indicator for evaluating the dynamics and scale of coastal dunes. However, the conventional two-dimensional cross-sectional area method has limitations in spatial representativeness due to its reliance on a single transect. This study presents a three-dimensional volumetric method for precise measurement of coastal dune topography and quantitative estimation of foredune sand volume using drone LiDAR. Multiple cross-sections were extracted from high-resolution digital elevation models to generate foredune toe and crest lines, from which sand volume was calculated. Field surveys were conducted at Cheotguji Dune during autumn and winter of 2024. The results revealed changes in total sand storage caused by the winter monsoon storm and spatial variations in erosion and deposition along the foredune ridge. The procedure presented in this study can be applied to advance coastal dune monitoring systems.
- COLLAPSE
해안사구는 자연방파제 역할과 생물다양성 유지 등 중요한 생태계 서비스를 제공하며, 이러한 기능의 핵심 요소는 전사구의 모래량이다. 우리나라에서는 전사구 모래량을 해안사구의 역동성과 규모를 평가하는 핵심 지표로 활용하고 있으나, 기존의 횡단면 기반 2차원 면적법은 단일 측선을 사용하여 공간적 대표성에 한계가 있었다. 본 연구에서는 드론 라이다를 활용하여 해안사구의 미세 지형을 정밀 측정하고, 전사구 모래량을 입체적으로 산정하는 3차원 체적법을 제시하였다. 고해상도 수치표고모델로부터 다수의 횡단면을 추출하여 전사구시점열과 사구마루열을 생성한 후 체적을 산정하였다. 신안군 첫구지사구를 대상으로 2024년 가을과 겨울에 현장조사를 수행한 결과, 북서계절풍에 의한 총 모래 저장량의 변화와 전사구열을 따른 침식·퇴적의 공간적 변이를 확인하였다. 본 연구에서 제시한 표준화된 절차는 향후 국내 해안사구 모니터링 고도화에 활용될 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
Three-Dimensional Estimation of Foredune Sand Volume in Coastal Dunes Using Drone LiDAR
Journal Informaiton
 Ecology and Resilient Infrastructure
Ecology and Resilient Infrastructure
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Ecology and Resilient Infrastructure
Ecology and Resilient Infrastructure










